
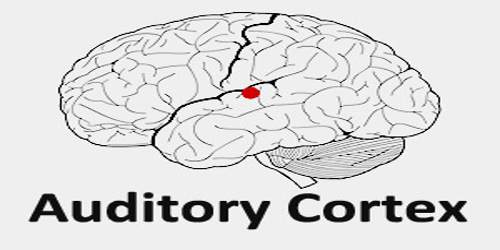
Here are two illustrations, without and with the context of the surrounding cortex: Table 25 Auditory cortex. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". Auditory cortex has traditionally been subdivided into primary (A1), secondary (A2) and tertiary (A3) areas, though nowadays this terminology has been replaced by core, belt and parabelt, respectively. This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. Located in the temporal lobe, a part of the cerebral cortex. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. Auditory Cortex is the section of the brain that processes information received through hearing. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics".
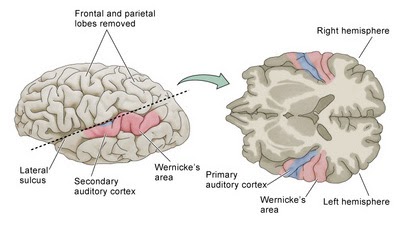
It corresponds to the transverse gyrus of Heschl. The primary auditory cortex (A1) is located in the upper bank of the temporal lobe and surrounded by specific auditory and nonspecific association areas. This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. Where is the auditory system located It is composed of primary auditory cortex (core) and associated auditory belt regions. These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website, anonymously. Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. It lies in the posterior half of the superior temporal gyrus and also dives into the lateral sulcus as the transverse temporal gyri also called Heschl’s gyri. The primary auditory cortex is about the same as Brodmann areas 41 and 42. Which is the correct pathway for auditory processing?Īuditory messages are conveyed to the brain via two types of pathway: the primary auditory pathway which exclusively carries messages from the cochlea, and the non-primary pathway (also called the reticular sensory pathway) which carries all types of sensory messages. The auditory cortex is located on the lateral surface in the temporal lobe of the brain. It is made up of both peripheral structures (e.g., outer, middle, and inner ear) and brain regions (cochlear nuclei, superior olivary nuclei, lateral lemniscus, inferior colliculus, medial geniculate nuclei, and auditory cortex). The auditory system processes how we hear and understand sounds within the environment. Once the hair fibres of the cochlea, the snail shell-resembling organ of the inner ear, have sent electrical signals to the auditory nerve, these impulses are transferred to the auditory centre of the brain. Many small neurons located in the brain are responsible for the processing of auditory information.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
